Petroleum is vital to many industries, and is of importance to the maintenance of industrialized civilization itself, and thus is a critical concern for many nations. The world consumes 30 billion barrels (4.8 km³) of oil per year, with developed nations being the largest consumers.. The production, distribution, refining, and retailing of petroleum taken as a whole represents the world's largest industry in terms of dollar value. The Oil and Gas includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transporting (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing petroleum products. The largest volume products of the industry are fuel oil and gasoline (petrol). Petroleum (oil) is also the raw material for many chemical products, including pharmaceuticals, solvents, fertilizers, pesticides, and plastics.
The AmericanPetroleum Institute divides the petroleum industry into five sectors:
1. Upstream (exploration, development and production of crude oil or natural gas)2. Downstream (oil tankers, refiners, retailers and consumers)3. Pipeline4. Marine5. Service and supply.
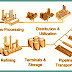
The industry is usually divided into three major components: upstream, midstream and downstream. Midstream operations are usually included in the downstream category. Upstream: The upstream oil sector is also commonly known as the exploration and production (E&P) sector.Operations stages in the oil and gas industry that involve exploration and production. Upstream operations deal primarily with the exploration stages of the oil and gas industry, with upstream firms taking the first steps to first locate, test and drill for oil and gas. Later, once reserves are proven, upstream firms will extract any oil and gas from the reserve.
 |
| Oil and Gas Upstream, Downstream and Midstream |
With the development of methods for extracting methane from coal seams, there has been
a significant shift toward including unconventional gas as a
part of the upstream sector, and corresponding developments in liquefied natural gas
(LNG) processing and transport.
Most upstream work in the oil field or on an oil well is contracted out to drilling contractors and oil field service companies.
Midstream: Midstream activities are commonly included as part of downstream operations for much of the oil and gas industry. The midstream and downstream activities take place after the initial production phase and through to the point of sale.
Midstream activities include the processing, storing, transporting and marketing of oil, natural gas and natural gas liquids.Oil and gas are transported to processing facilities, and from there to end users, by pipeline, tanker/barge, truck, and rail. Midstream service providers provide storage facilities at terminals throughout the oil and gas distribution systems.
Downstream: The oil and gas operations that take place after the production phase, through to the point of sale. Downstream operations can include refining crude oil and distributing the by-products down to the retail level. By-products can include gasoline, natural gas liquids, diesel and a variety of other energy sources.The downstream sector touches consumers through products such as gasoline or petrol, kerosene, jet fuel, diesel oil, heating oil, fuel oils, lubricants, waxes, asphalt, natural gas, and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as well as hundreds of petrochemicals.
Midstream operations are often included in the downstream category and considered to be a part of the downstream sector while implementing the SAP for the Oil and Gas company.
Most large oil companies are known as "integrated" because they combine upstream activities with midstream and downstream operations, which take place after the production phase through to the point of sale.